Mesenchymal stem cells alleviate acute liver failure through regulating hepatocyte apoptosis and macrophage polarization
Acute liver failure (ALF) is a life-threatening clinical problem with limited treatment options. Administration of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (hUC-MSCs) may be a promising approach for ALF. This study aimed to explore the role of hUC-MSCs in the treatment of ALF and the underlying mechanisms.
Credit: Enqiang Chen, Hong Tang, Yachao Tao
Background and Aims
Acute liver failure (ALF) is a life-threatening clinical problem with limited treatment options. Administration of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (hUC-MSCs) may be a promising approach for ALF. This study aimed to explore the role of hUC-MSCs in the treatment of ALF and the underlying mechanisms.
Methods
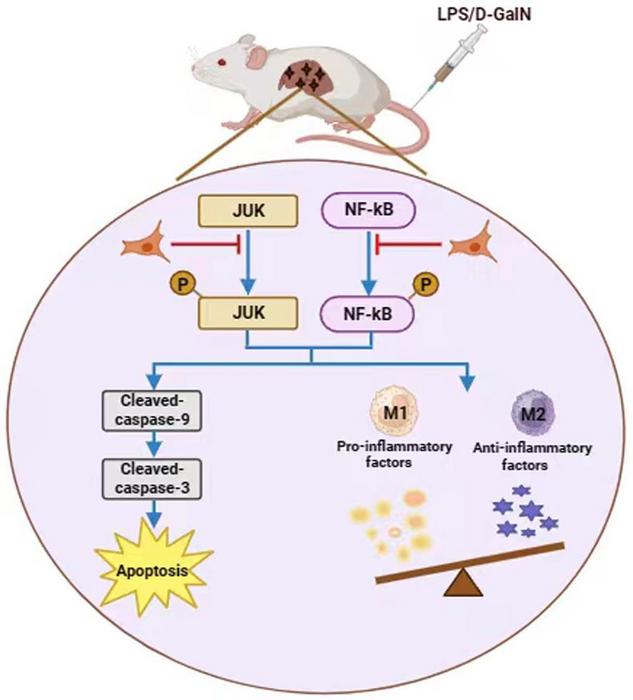
A mouse model of ALF was induced by lipopolysaccharide and d-galactosamine administration. The therapeutic effects of hUC-MSCs were evaluated by assessing serum enzyme activity, histological appearance, and cell apoptosis in liver tissues. The apoptosis rate was analyzed in AML12 cells. The levels of inflammatory cytokines and the phenotype of RAW264.7 cells co-cultured with hUC-MSCs were detected. The C-Jun N-terminal kinase/nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathway was studied.
Results
The hUC-MSCs treatment decreased the levels of serum alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase, reduced pathological damage, alleviated hepatocyte apoptosis, and reduced mortality in vivo. The hUC-MSCs co-culture reduced the apoptosis rate of AML12 cells in vitro. Moreover, lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 cells had higher levels of tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-6, and interleukin-1β and showed more CD86-positive cells, whereas the hUC-MSCs co-culture reduced the levels of the three inflammatory cytokines and increased the ratio of CD206-positive cells. The hUC-MSCs treatment inhibited the activation of phosphorylated (p)-C-Jun N-terminal kinase and p-nuclear factor-kappa B not only in liver tissues but also in AML12 and RAW264.7 cells co-cultured with hUC-MSCs.
Conclusions
In summary, hUC-MSCs can alleviate ALF by inhibiting hepatocyte apoptosis and regulating macrophage polarization, and thus, hUC-MSC-based cell therapy may serve as an alternative option for patients with liver failure.
Full text
https://www.xiahepublishing.com/2310-8819/JCTH-2023-00557
The study was recently published in the Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology.
The Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology (JCTH) is owned by the Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University and published by XIA & HE Publishing Inc. JCTH publishes high quality, peer reviewed studies in the translational and clinical human health sciences of liver diseases. JCTH has established high standards for publication of original research, which are characterized by a study’s novelty, quality, and ethical conduct in the scientific process as well as in the communication of the research findings. Each issue includes articles by leading authorities on topics in hepatology that are germane to the most current challenges in the field. Special features include reports on the latest advances in drug development and technology that are relevant to liver diseases. Regular features of JCTH also include editorials, correspondences and invited commentaries on rapidly progressing areas in hepatology. All articles published by JCTH, both solicited and unsolicited, must pass our rigorous peer review process.
Follow us on X: @xiahepublishing
Follow us on LinkedIn: Xia & He Publishing Inc.
Journal
Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology
DOI
10.14218/JCTH.2023.00557
Article Title
Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate Acute Liver Failure through Regulating Hepatocyte Apoptosis and Macrophage Polarization
Article Publication Date
30-Apr-2024